CBP 2025 Outlook
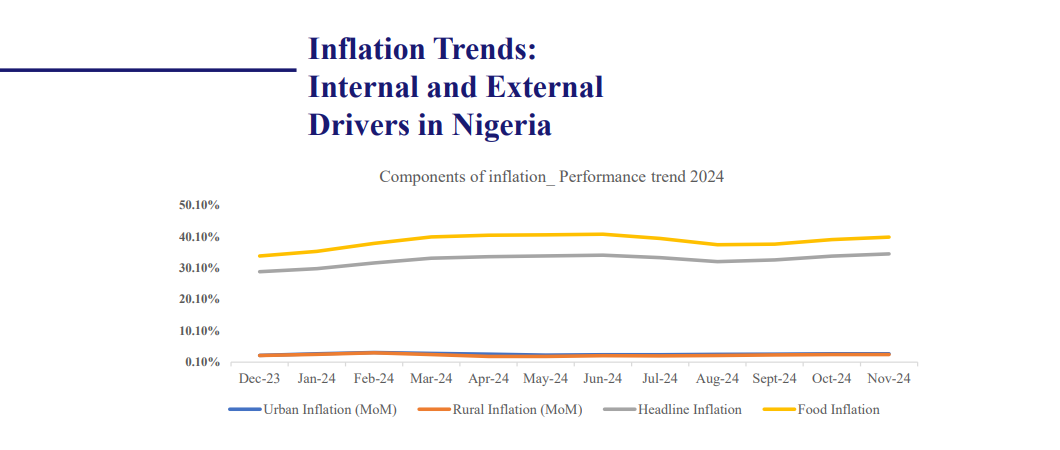
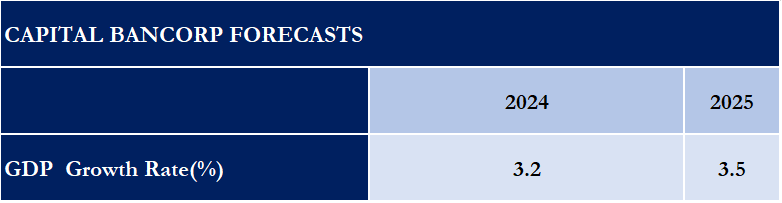
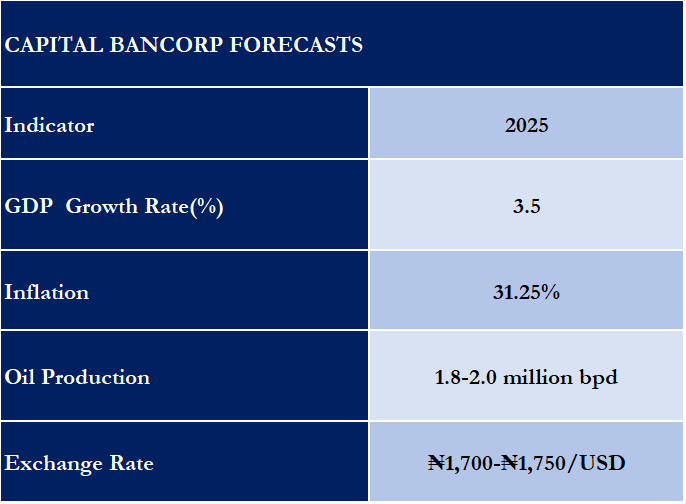
Nigeria's economy is expected to grow by 3.5% and 3.68% (MTF) in 2025, driven by structural reforms, infrastructure investments, and a recovering oil sector. The services sector remains the dominant contributor to GDP, particularly telecommunications, fintech, and trade, benefiting from regional integration under AfCFTA. Agriculture is also expected to see gains through mechanization and climate adaptation efforts. However, key risks persist, including high inflation (34.80% as of October 2024), currency volatility due to naira depreciation, and external shocks from fluctuating oil revenues. Fiscal challenges remain, with government policies focused on increasing non-oil revenue and improving macroeconomic stability.
Key Growth Drivers:
• Expansion in services, fintech, and telecommunications.
• Agriculture growth through improved irrigation and mechanization.
• Oil production recovery to 1.8 – 2.0 million bpd, supported by security improvements and reduction in oil theft.
Nigeria's economy is set for mixed growth across key sectors, with varying opportunities and challenges shaping the outlook for 2025. In the Oil and Gas sector, production is expected to recover to 1.8-2.0 million barrels per day after a decline in 2024. Brent crude prices are projected to stabilize at $76 per barrel, influenced by OPEC+ production cuts and the global energy transition. The Dangote Refinery is anticipated to enhance supply chain efficiency and reduce reliance on imports. Although, the manufacturing sector continues to grapple with energy shortages and high production costs. However, local content policies and the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) present opportunities for industrial growth, particularly in textiles, agro-processing, and consumer goods. Agriculture remains a key contributor to the economy, accounting for 24% of GDP in Q3 2024. Growth in the sector is driven by mechanization, improved irrigation, and enhanced logistics. Key commodities like cocoa, cassava, and rice are expected to perform well, though climate-related risks pose challenges.
In the Financial services, Banking sector recapitalization is expected to strengthen lending capacity and overall stability. The continued expansion of digital banking and fintech solutions is driving financial inclusion, with mobile banking adoption also on the rise.
Policy & Fiscal Outlook
Government Strategies & Budget Priorities
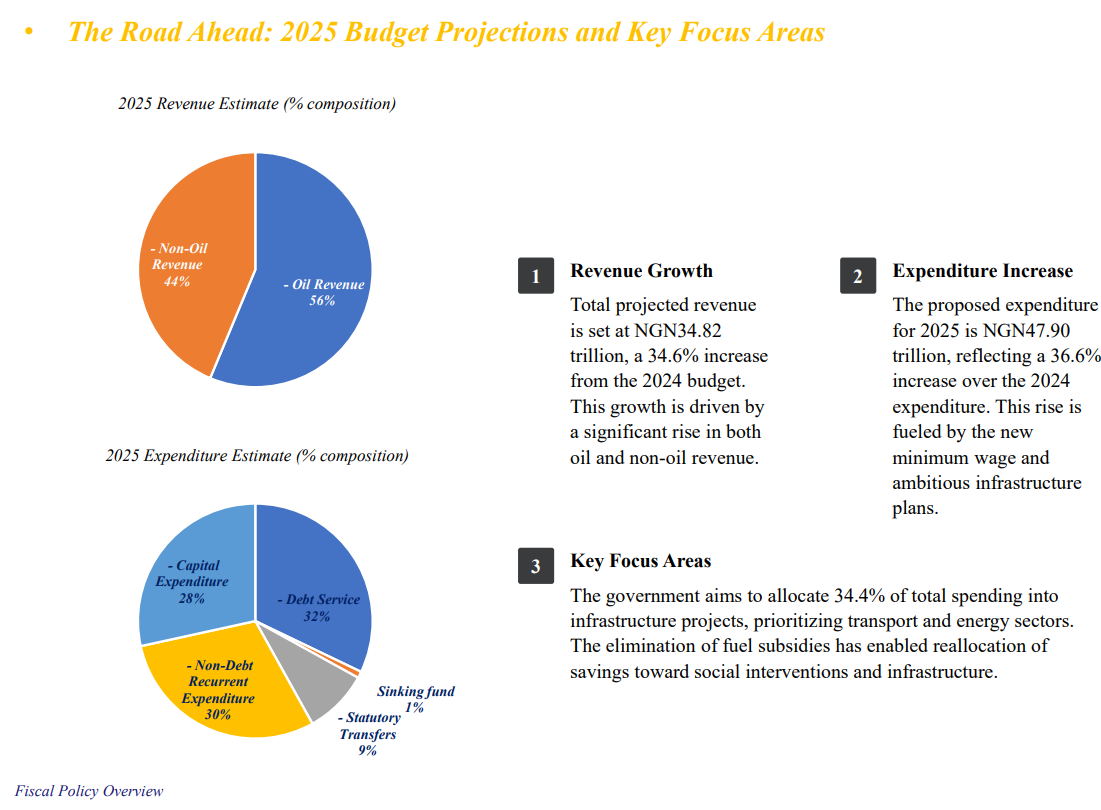
The 2025 budget is set at NGN 47.9 trillion, with increased spending on infrastructure, healthcare, and education. Debt servicing remains a significant expenditure, accounting for NGN17.6 trillion (36.7% of total spending). The government aims to boost revenue through tax reforms, VAT adjustments, and digital taxation.
Key Risks & Disruptions
• Inflationary Pressures: High cost of living due to fuel subsidy removals and food price surges.
• Exchange Rate Volatility: Naira depreciation affecting import-dependent sectors.
• Oil Price Fluctuations: Global energy market shifts impacting government revenues.
• Debt Sustainability: Rising debt burden limiting fiscal space.
• Climate Risks: Unpredictable weather patterns affecting agricultural output.
Policy & Fiscal Outlook
While Nigeria faces significant economic challenges, targeted reforms, infrastructure investments, and private sector expansion provide a path toward stable growth in 2025 and beyond. The country’s ability to navigate inflation, currency risks, and external shocks will determine its economic resilience moving forward.